Texture is an essential element of art that can be both tactile and visual.
It refers to the way the surface of an artwork looks or feels, and it can be smooth, rough, bumpy, or even prickly.
Texture can add depth and dimension to an artwork, creating a sense of realism or abstraction. Understanding texture is crucial for artists, as it can greatly influence the mood and emotion conveyed in a piece of art.
It can also be used to create contrast and balance in a composition, drawing attention to certain areas of the artwork.
Texture is not limited to just paint or sculpture but can also be found in photography and digital art.
But let’s go over what you can do with texture, one of the 7 elements of art! (as well as few examples at the end of this article!)
Table Of Contents
Key Takeaways
- Texture in art refers to the way the surface of an artwork looks or feels, and it can be both tactile and visual.
- Texture can greatly influence the mood and emotion conveyed in a piece of art, and it can be used to express different emotions, from softness to roughness.
- There are two types of texture in art: tactile and visual. Tactile texture is the physical texture that can be felt by touching the surface of a work of art, while visual texture is an illusion of texture created by the artist.
- Texture can be used to create contrast within a piece. Highlighting certain elements and drawing attention to specific areas. And it can be found in various mediums and styles, from classical sculptures to impressionist paintings.
What Is Texture?

Texture is like the spice in a recipe, adding depth and flavor to the otherwise bland canvas.
In art, texture refers to the surface quality of a work of art that can be seen and felt. It’s one of the seven elements of art, along with line, shape, form, color, value, and space.
Texture can be created in various ways, such as through the use of different materials, brushstrokes, or techniques.
And there are two types of texture in art: tactile and visual.
Tactile texture is the physical texture that can be felt by touching the surface of a work of art.
Visual texture, on the other hand, is an illusion of texture created by the artist. It’s the way the surface of a work of art appears to feel, even though it cannot be physically touched.
This can also be called an implied texture!
Visual texture can be created through the use of shading, patterns, or other techniques that create elements to create the illusion of form and create a sense of depth!
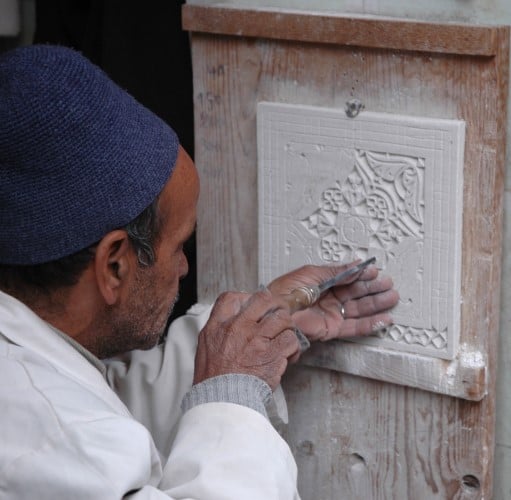

Physical texture is an important aspect of tactile texture. It refers to the actual surface quality of a work of art, such as roughness, smoothness, or softness.
You can create physical texture by using different materials, such as sand, paper, or fabric, or by applying thick layers of paint.
By incorporating physical texture into their works of art, artists can add a sense of dimension and realism to their works.
With this understanding of texture in art, let’s explore how artists use texture in their work.
Using Texture in Art
As you look at a painting, you’ll notice the subtle use of rough brushstrokes that symbolize the turmoil and chaos of the subject’s emotions.
As well as simple soft strokes to create an appealing and calm look to the art piece!
Here are five ways that artists use texture in their painting techniques to evoke an emotional response from their audience:
- Creating rough brushstrokes to convey the feeling of anxiety or chaos.
- Using smooth brushstrokes to depict calmness or serenity.
- Adding impasto to the paint to create a three-dimensional effect.
- Applying different textures to the surface of the canvas to create a tactile experience.
- Using contrasting textures to create a sense of tension or conflict.
Texture in art can be achieved through a variety of mediums, including paint, mixed media, and sculpture.
By using different textures in their artwork, artists can create a multi-sensory experience that engages the viewer on both a visual and tactile level.
It’s a great point to keep in mind when working on an art piece’s composition.
Texture in art is not only an important element of the visual experience of a work of art, but it can also evoke a powerful emotional response from the audience.
In the next section, we’ll explore how texture and emotion are intertwined in art.
Texture and Emotion
By incorporating different textures into their artwork, artists are able to elicit a range of emotional responses from their audience, creating a multi-dimensional experience that engages both the senses and the soul.

Texture plays a crucial role in conveying emotion in art.
For example, rough, jagged textures can evoke feelings of tension or unease, while soft, smooth textures can create a sense of calm and tranquility.
Texture can also be used to create contrast within a piece, highlighting certain elements and drawing attention to specific areas.
By using texture in their work, artists are able to create a multi-layered experience that engages the viewer on both a visual and emotional level.
In the next section, we’ll explore how texture is used in different mediums, from painting to sculpture to photography.
Texture in Different Mediums
When you touch a sculpture, you can feel the grooves and curves of the material! This adds a physical dimension to the artwork.
This tactile quality creates a three-dimensional effect that adds to the overall experience of the artwork.
Texture can be found in both two-dimensional and three-dimensional mediums, each with its own unique approach.
In painting techniques, texture is created by adding substances to the paint, such as sand or grit, to create a rough surface. This technique is called impasto and is commonly used in the works of Vincent van Gogh.
In two-dimensional mediums such as drawing or printmaking, artists use techniques such as cross-hatching or stippling to create the illusion of texture on a flat surface.
Some other methods include the use of brushstrokes, applying thick paint with a palette knife, hatching or cross-hatching for drawing and painting,
The manipulation of light and angle also plays a significant role in creating a textural appearance.
In contrast, texture in sculpture is created by carving into the surface or adding material to create a raised surface.
The use of texture in sculpture can add depth and dimensionality to a piece, transforming it from a static object into a dynamic and engaging work of art.
When working with three-dimensional mediums, artists can experiment with different materials such as gesso, marble, or coarse surfaces.
Examples Of Texture in Art
You can experience the rough, jagged texture of Edvard Munch’s ‘The Scream’ in person at the National Gallery in Oslo.
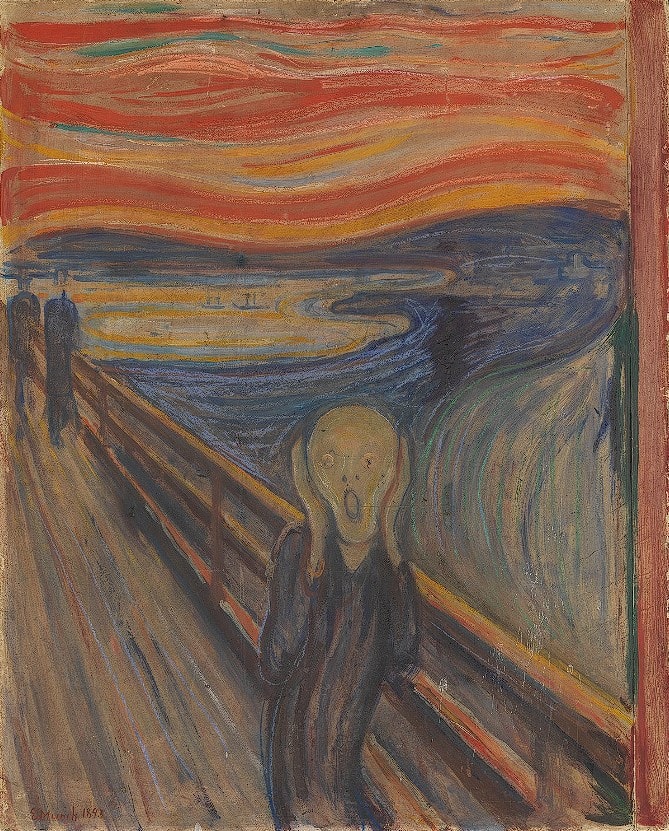

The texture in this iconic painting is a prime example of how artists use texture to create visual interest and depth in their work.
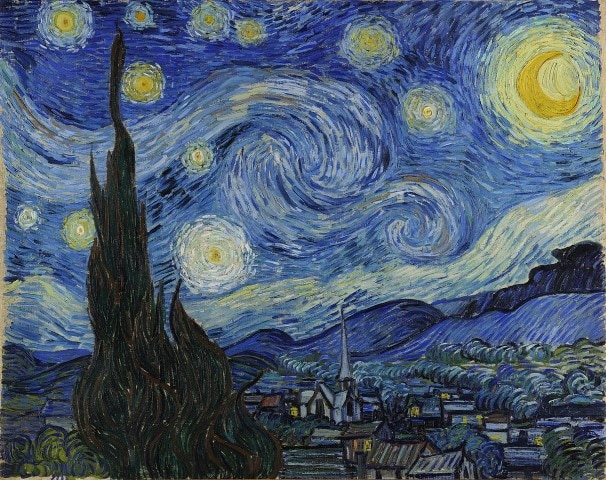
Texture can also be used to create contrast, such as in Vincent van Gogh’s ‘Starry Night’ where the swirling, textured sky contrasts with the smooth, flat buildings below.

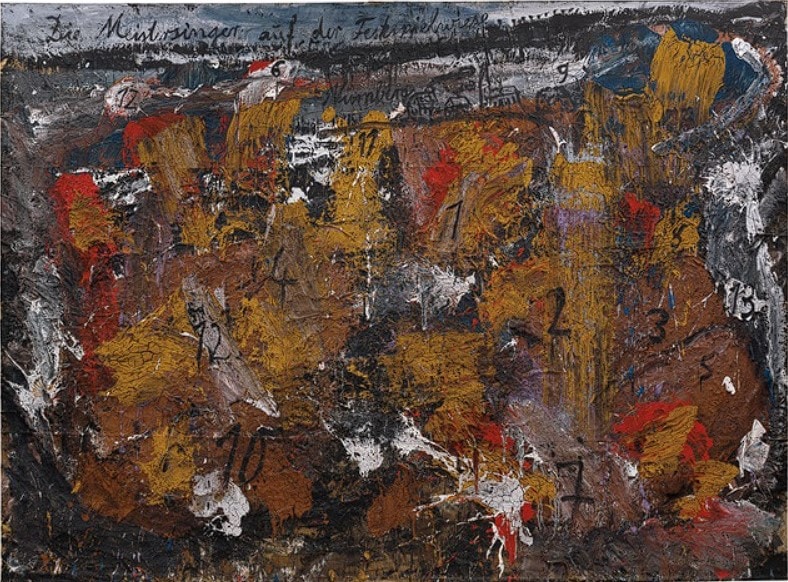
Incorporating texture into art can also be a way to push the boundaries of innovation. For instance, contemporary artists like Anselm Kiefer use unconventional materials like straw, ash, and lead to create textured surfaces that challenge traditional notions of what art can be.

Another example of a rough texture includes the works of Claude Monet. This artist often used a palette knife to apply thickly painted brushstrokes to create textured and rough surfaces in his paintings.

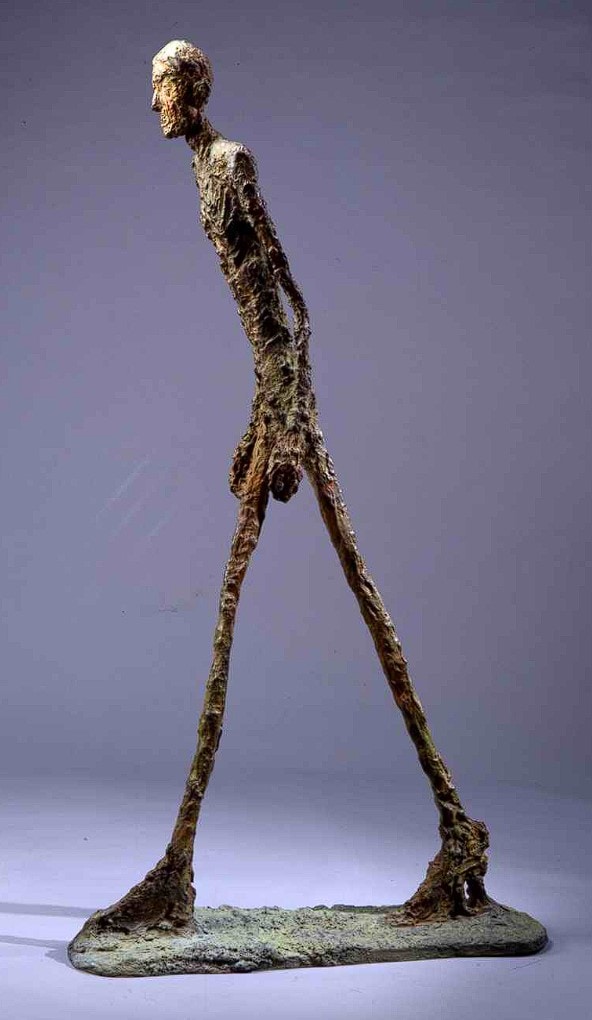
Other examples could be Alberto Giacometti‘s sculptures, which have a gritty, coarse texture due to the materials and techniques he used.

Whether it’s using texture to evoke certain emotions or experimenting with new materials to create innovative textures, artists continue to push the boundaries of what texture in art can be.
Related Questions
So what else there is to know about texture in art?
Well, quite a bit! So let’s go over a few related questions to this art element.
Why is texture considered a fundamental element?
Texture is one of the elements of art that refers to the surface quality of a piece of work.
It could be depicted through physical texture or the illusion of texture.
It’ is’s a fundamental element because it adds depth, and interest, and helps connect the viewer to the art piece through the sense of touch.
What are the two types of texture in art?
The two types of texture in art are physical texture and visual (illusion) texture.
Physical texture refers to the actual surface of the piece, while visual texture represents the appearance or the illusion of texture on a flat, two-dimensional surface.
What is the difference between a glossy and a matte texture?
A glossy texture is shiny and reflects light, giving a smooth and polished appearance.
In contrast, a matte texture has a dull, flat surface that doesn’t reflect light and appears more subdued.
Both textures can be used effectively in various art forms to create different effects and evoke different emotions.
For more information about the other elements of art, be sure to check this article on the 7 Elements Of Art (With Examples)!
And to get some great materials to create texture, check out this list!
Patricia Caldeira is the main writer here at Don Corgi. She's an art teacher with over 20.000 happy students across many platforms and courses!
Enjoy your stay and as always:
Keep on drawing!



